Perfect_B_Matching
This example shows how to compute a perfect B matching of a given graph G using the symbolic constraint SCIL::MATCHING.We first create an empty graph and initialize it using either the function readgraph or readgraphFromTSPLIB whichs reads a TSPLIB instance.
Graph G; map<vertex_descriptor, int> node_mapG; map<edge_descriptor, double> edge_mapG; map<vertex_descriptor, int> nc; //if( !readgraph(base, argv[1], G, nc) ) if( !readgraphFromTSPLIB(writeout, base, argv[filearg], G, nc, node_mapG,
ILP_Problem IP(Optsense_Min);
edge_descriptor e; var_map<edge_descriptor> VM; BGL_FORALL_EDGES(e, G, Graph) { vl.push_back(IP.add_binary_variable(edge_mapG[e])); VM[e] = vl.back(); }
map<vertex_descriptor, int> nc is used to store for each node the number of adjacent edges in the matching. The edges corresponding to variables with value 1 in an optimal solution should form a valid matching in G. To achieve this we add the symbolic constraint SCIL::MATCHING to the model. IP.add_sym_constraint(new MATCHING<Graph>(G, nc, VM));
optimize. IP.optimize();
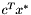 for the optimal solution
for the optimal solution 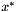 stored in
stored in sol. //output the solution solution sol = IP.get_solution(); double sum = 0.; cout << "\nName: " << argv[1] << endl; BGL_FORALL_EDGES(e, G, Graph) { sum += double(edge_mapG[e]) * sol.value(VM[e]); if( sol.value(VM[e]) > .9 ) { cout << node_mapG[source(e, G)] + base << " -- "; cout << node_mapG[target(e, G)] + base << endl; } } cout << endl; cout.precision(2); cout << fixed << "solution value: " << sum << endl;
 1.6.3
1.6.3